Out Of Specification(OOS)
Out-of-Specification (OOS) refers to a result or observation that falls outside the predetermined acceptance criteria or specifications established for a particular process, product, or material in the life sciences industry.
The significance of OOS findings lies in their potential impact on patient safety, product quality, and regulatory compliance. Identifying and appropriately addressing OOS results are crucial steps in maintaining the integrity of products, ensuring patient well-being, and complying with stringent regulatory requirements.

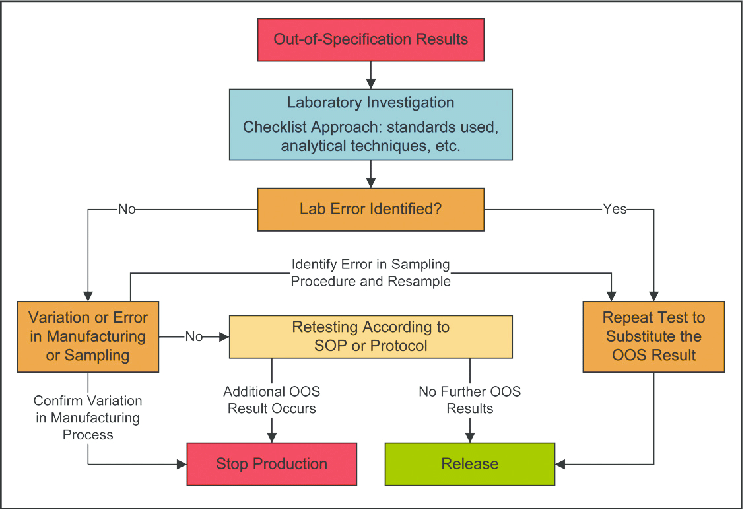
Investigation Processes for Out-of-Specification (OOS) Results
Documentation and Data Collection
When an OOS result is identified, a thorough investigation begins by documenting all relevant details, including sample information, test procedures, environmental conditions, and any other factors that may have influenced the result. Comprehensive data collection is crucial for subsequent analysis and investigation.
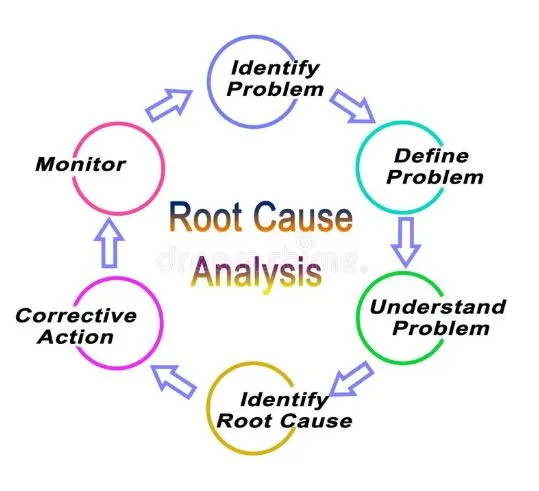
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is conducted to identify the underlying reason(s) for the OOS result. It involves a systematic examination of all possible factors, including analytical methods, instruments, samples, manufacturing processes, and raw materials, to determine the primary cause(s) contributing to the OOS situation.
While similar to operational qualification, performance qualification is used to verify that the equipment consistently produces the correct results under real-world conditions. That means PQ should be conducted in the actual facility with trained personnel, using the utilities, equipment, control procedures and manufacturing process that will be used to produce commercial batches of the product.

Regulatory Implications of Out-of-Specification (OOS) Findings
In the life sciences industry, OOS findings have significant regulatory implications. Regulatory authorities, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States or the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, require timely reporting and appropriate handling of OOS results.
To ensure compliance, companies in the life sciences industry are required to establish robust quality management systems, including thorough documentation, data integrity measures, proper investigation processes, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory guidelines.
Summary
Out-of-Specification (OOS) findings in the life sciences industry signify results falling outside the defined acceptance criteria or specifications. Recognizing and appropriately addressing OOS results are crucial to maintain the quality and safety of life science products and comply with stringent regulatory requirements.
Thorough investigation processes, including root cause analysis, repeat testing, and OOT analysis, facilitate the identification of underlying causes and the implementation of corrective and preventive actions. Compliance with regulatory reporting and handling procedures is essential to ensure regulatory compliance and maintain the trust and safety of patients and consumers.

