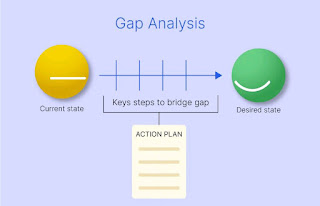
Gap Assessment
A way to compare current conditions and practices in order to identify gaps and areas in need of improvement with regards to compliance to the relevant standards.
Gap Analysis is one of the best procedures to help lead an organization to not only improve their processes, but recognize which processes are in need of improvement. In the highly regulated pharmaceutical and medical device industries, conducting a gap assessment is a crucial step towards ensuring compliance, quality, and patient safety.
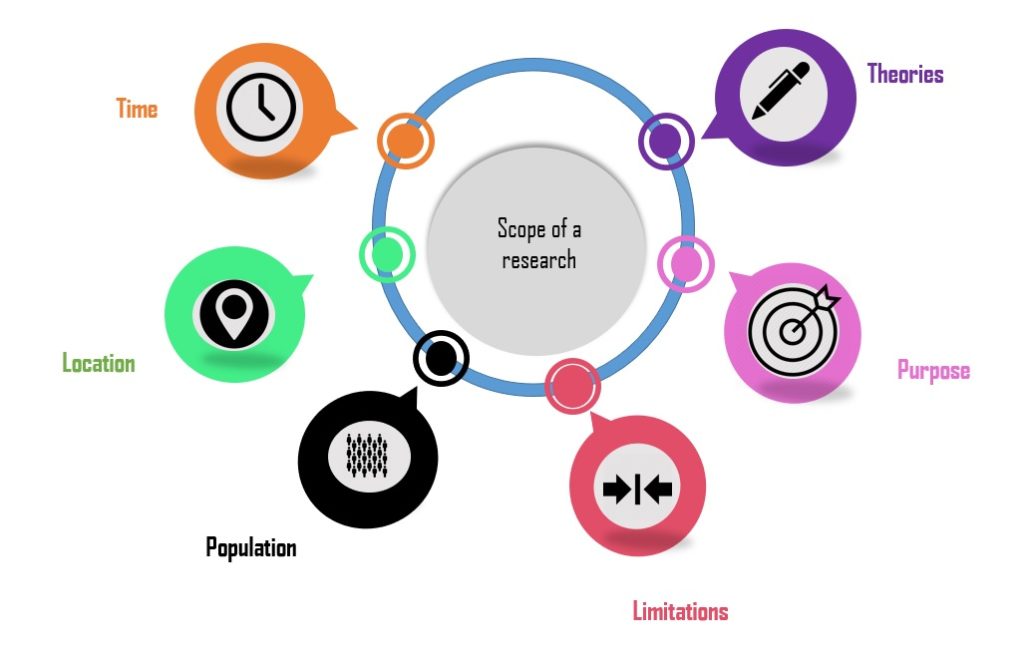
Define the Scope and Objectives
Before initiating a gap assessment, it is essential to clearly define the scope and objectives. Identify the specific regulations, standards, guidelines, and internal requirements that need to be evaluated. Determine the focus areas, such as quality management systems, manufacturing processes, product safety, data integrity, or supply chain management. Clearly outlining the scope and objectives will help streamline the assessment process and ensure its effectiveness.
Engage Cross-Functional Teams
A successful gap assessment requires the involvement of cross-functional teams representing various departments within the organization. Include representatives from quality assurance, regulatory affairs, research and development, manufacturing, and other relevant areas. This ensures a holistic evaluation and minimizes biases in identifying gaps and potential risks.
Conduct a Regulatory Landscape Review
Stay updated with the latest regulations, guidelines, and industry trends related to pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing. Understand the regulatory expectations of authorities such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) or the EMA (European Medicines Agency). Incorporate these requirements into the gap assessment process to ensure compliance and mitigate regulatory risks effectively.
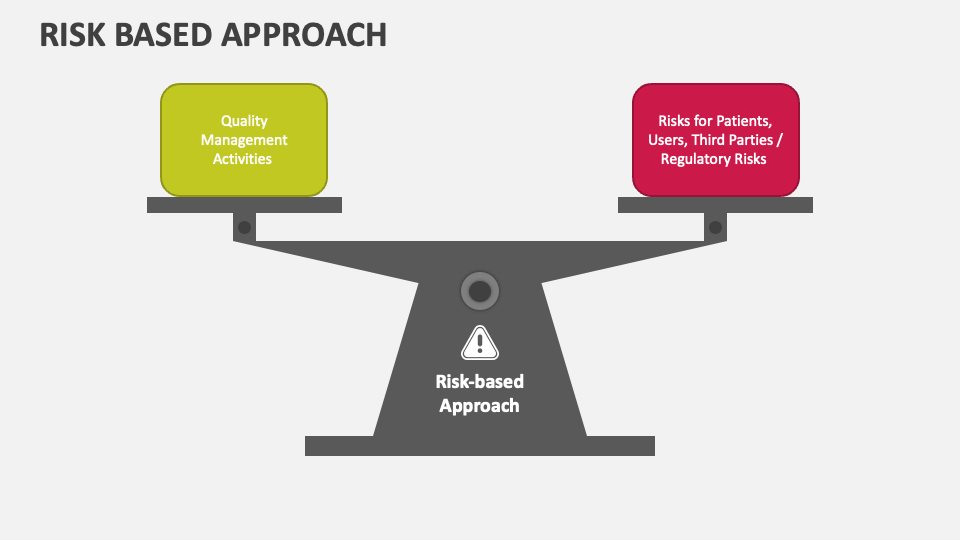
Utilize Risk-Based Approach
Adopting a risk-based approach is crucial for a thorough and efficient gap assessment. Identify the areas of highest risk based on criticality, impact on patient safety, regulatory non-compliance, and business impact. Prioritize these high-risk areas to focus resources and efforts effectively. Consider using risk assessment tools such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) or Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) to identify and evaluate risks.